var images = document.getElementsByTagName('img'); for (var i = 0; i < images.length; i++) { if (!images[i].getAttribute('alt')) { images[i].setAttribute('alt', ''); } }
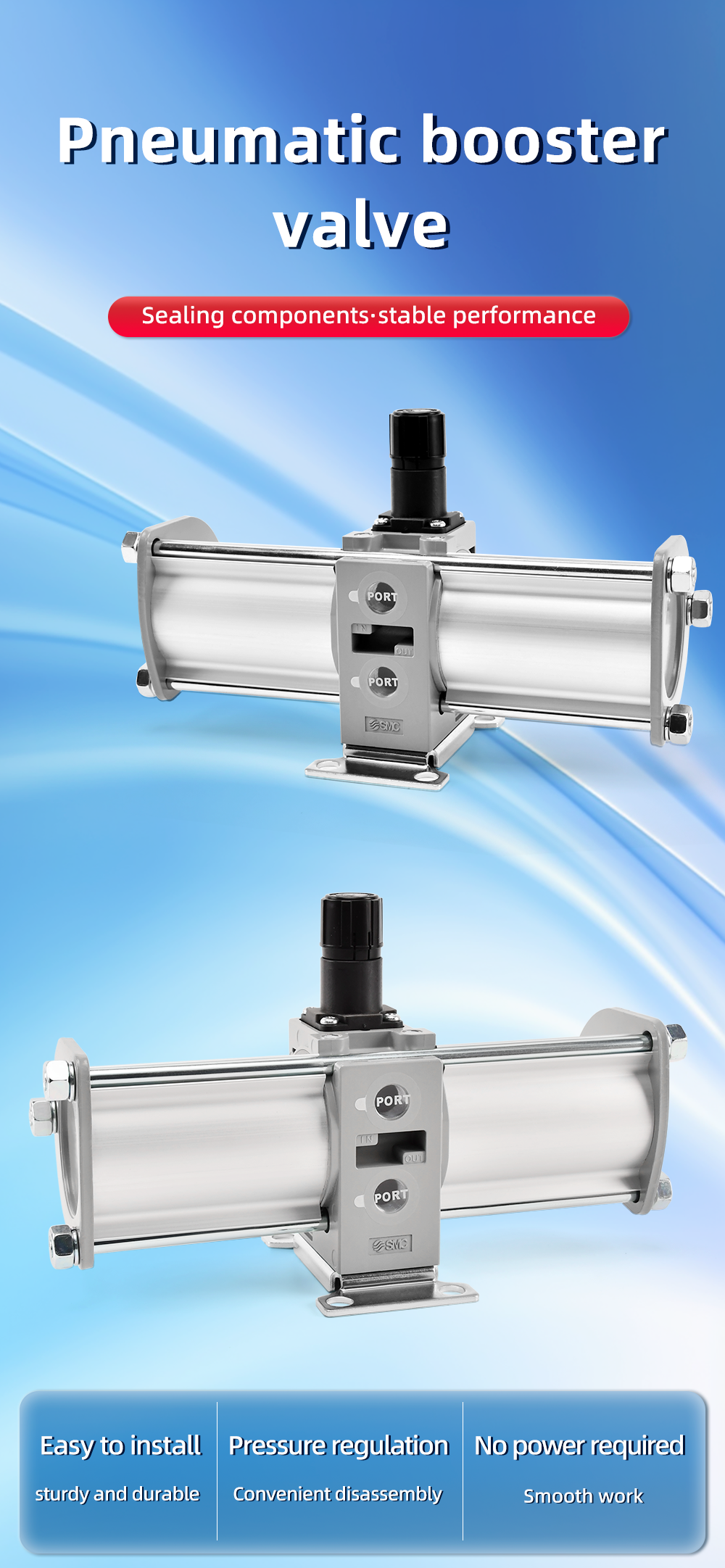
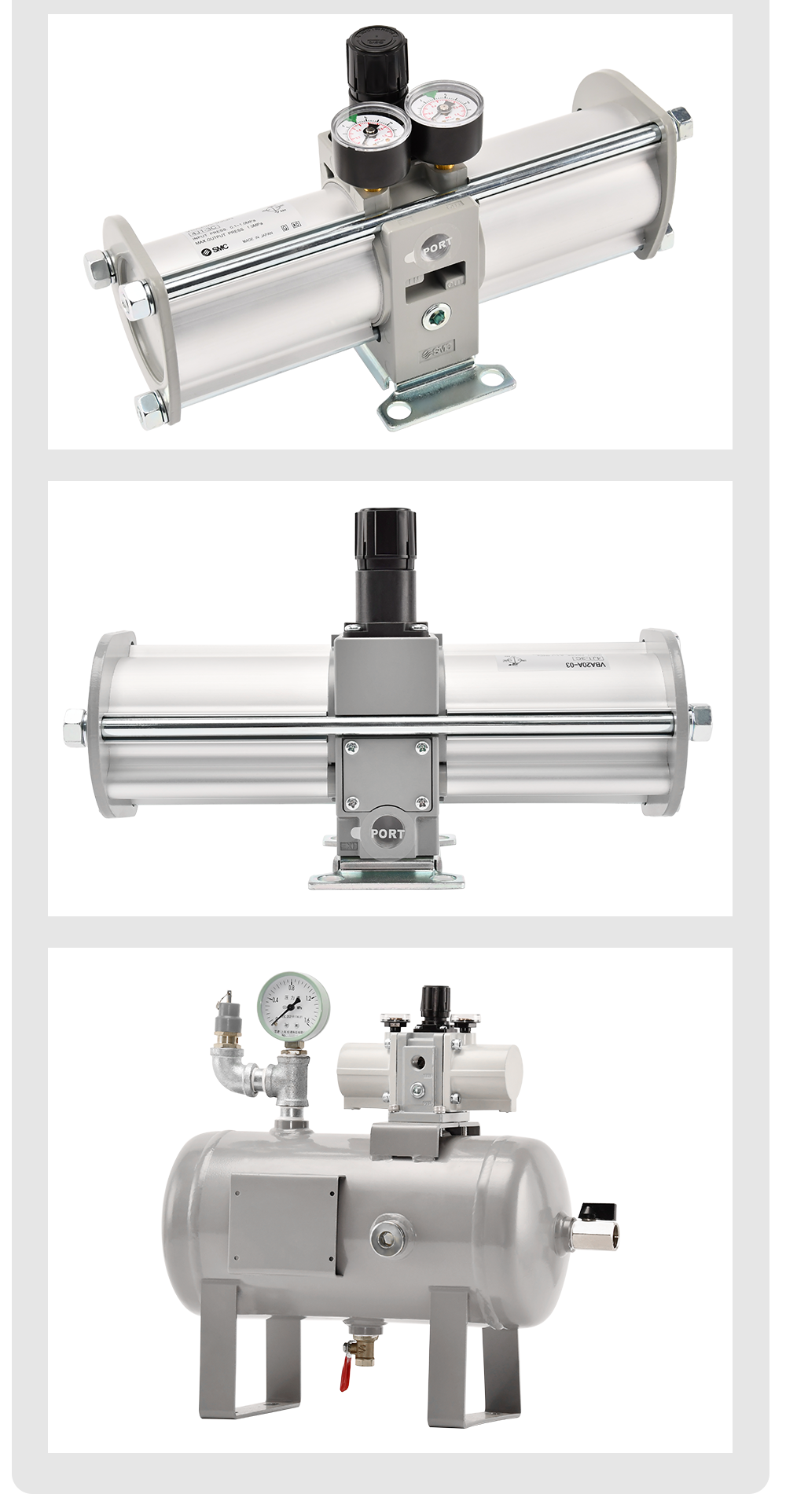






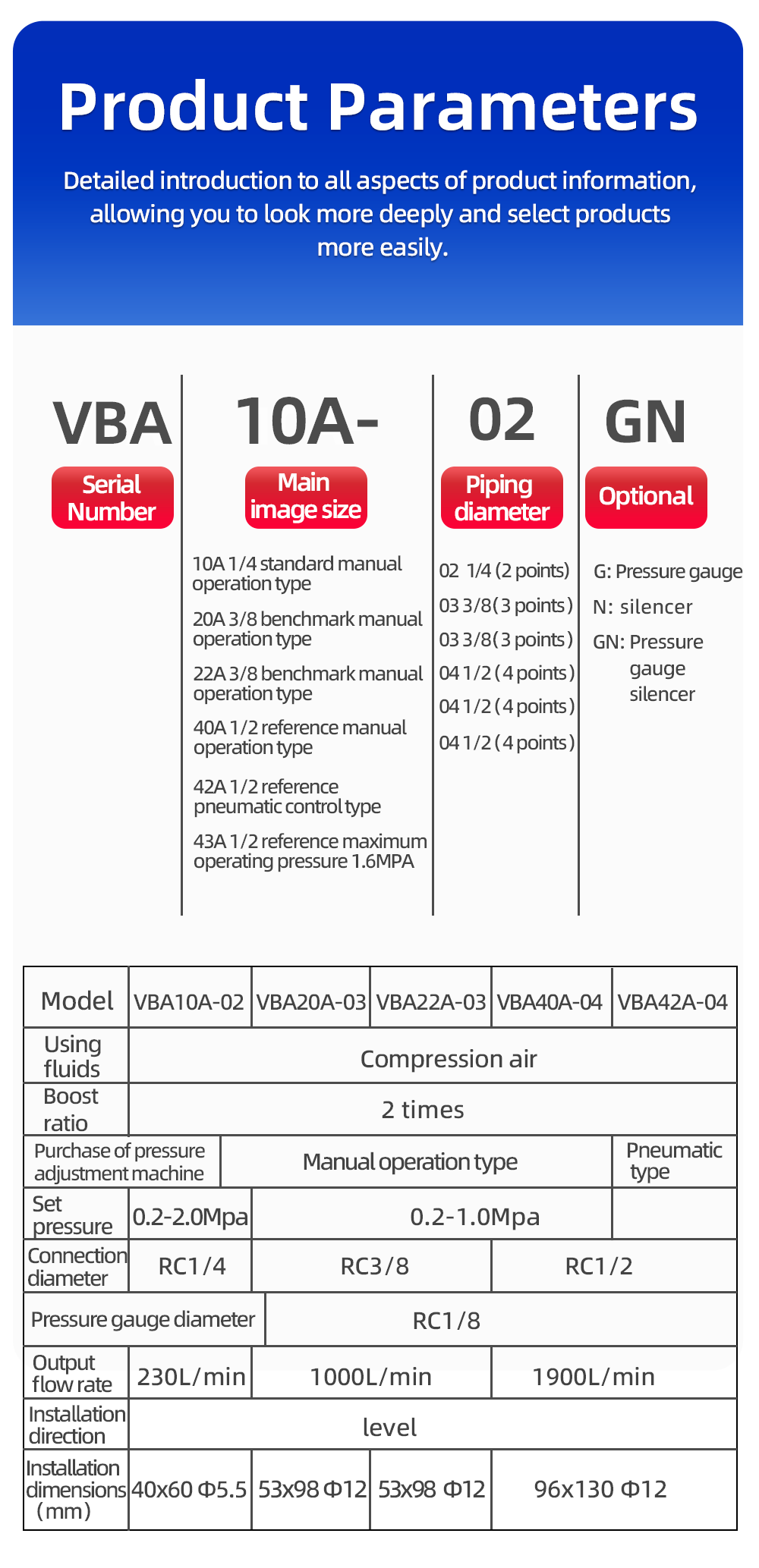




VBA Series Booster Valve with a 2:1 Boost Ratio.
This is a specific product line, most commonly associated with SMC Corporation, a leading manufacturer of pneumatic automation components.
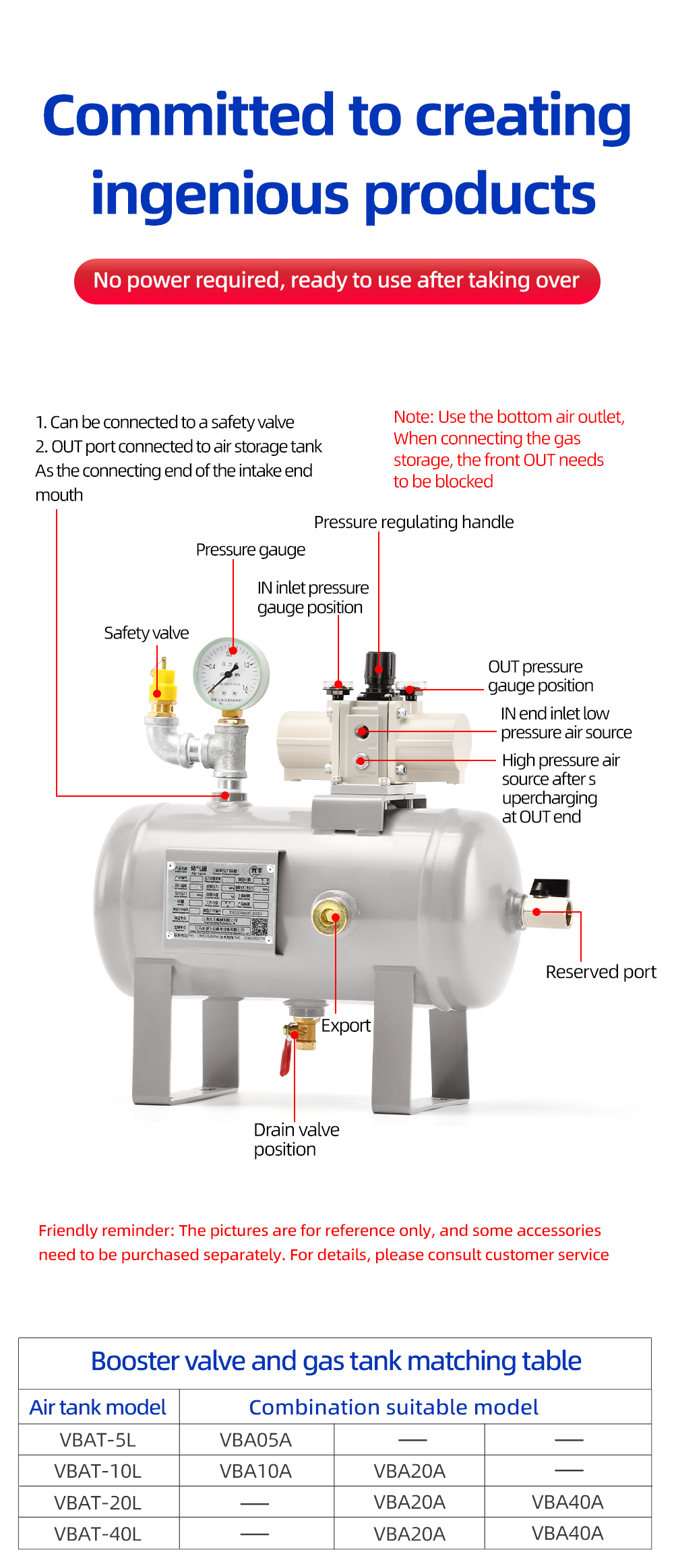
A booster valve is a pneumatic device that takes a lower supply pressure and increases it to a higher output pressure. It does this without the need for an electrical power source; it uses the air pressure itself, often with a pilot signal, to activate a large piston that drives a smaller piston.
Think of it like a mechanical lever for pressure: a large force (from the low-pressure, large-area piston) is converted into a smaller force acting on a much smaller area, resulting in a significant increase in pressure.
The boost ratio is the most critical specification. A 2:1 ratio means:
Output Pressure ≈ 2 x Pilot Pressure
How it works in practice:
Supply Pressure (P_s): This is the main shop air line connected to the booster, typically a standard pressure like 60-100 PSI (4-7 bar).
Pilot Pressure (P_p): This is the control signal pressure you apply to tell the booster to activate. It's usually a lower, easier-to-control pressure.
Output Pressure (P_o): This is the resulting high pressure delivered to your application.
The Formula: P_o ≈ 2 x P_p
Important Note: The output pressure P_ocan never exceed 2 x the supply pressure P_s. The booster can only amplify the pressure it is given.
Example:
Your Supply Pressure (P_s) is a constant 80 PSI.
You apply a Pilot Pressure (P_p) of 40 PSI to the control port.
The Output Pressure (P_o) will be ≈ 2 x 40 PSI = 80 PSI.
If you need a higher output, you must increase the pilot pressure (up to the limit of the supply pressure).
While exact specs depend on the specific model (e.g., VBA20A, VBA40A), here are general characteristics:
Boost Ratio: 2:1 (as discussed)
Maximum Supply Pressure (P_s): Often around 150 PSI (10 bar).
Maximum Output Pressure (P_o): Since it's a 2:1 booster, this is typically 300 PSI (20 bar). This is its most common use case—taking standard shop air (~100 PSI) and boosting it to a higher pressure for special applications.
Port Size: Common sizes are 1/8", 1/4", or 3/8" NPT.
Construction: Aluminum body.
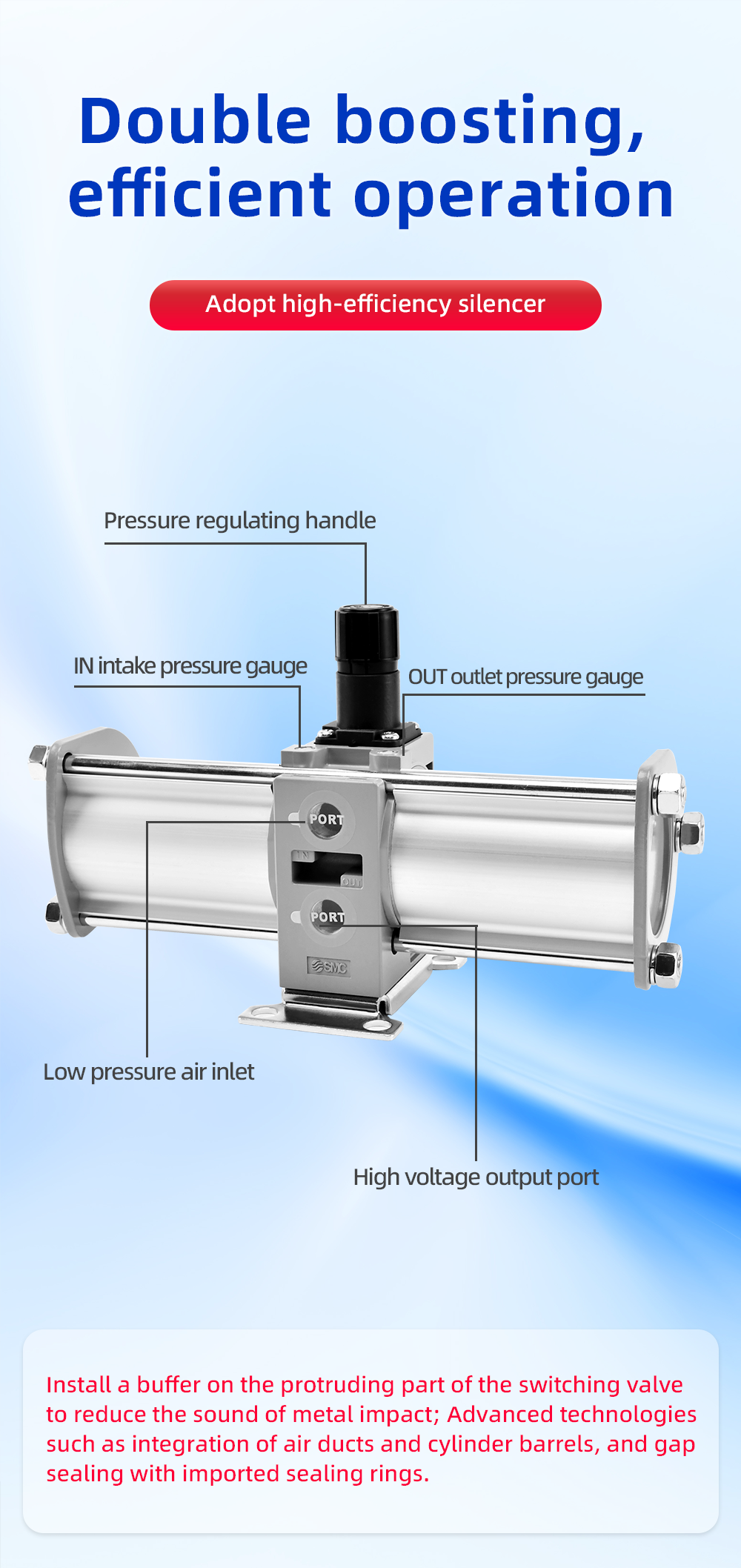
Function: Usually 3-port, 2-position. It has a supply port, an output port, and an exhaust port. When the pilot signal is applied, it connects supply to output. When the pilot signal is removed, it vents the output to the exhaust port.
These devices are used when a machine has standard low-pressure air but one or two functions require a higher pressure. Running the entire system at high pressure would be inefficient and dangerous.
High-Pressure Clamping: Generating very high holding forces with a small pneumatic clamp or cylinder.
Air-Driven Pumps: Pressurizing the pilot signal for hydraulic pumps or other intensifiers.
Pneumatic Tool Actuation: Operating valves or actuators that require a higher pressure signal than what is available in the main system.
Balancing Pressures: In systems with long lines where pressure drop is an issue, a booster can be used locally to regain the required operating pressure.
Testing: Pressurizing a component for a leak test or a proof test at a pressure higher than the main line air.
Lubricated Air: Many boosters, especially older models, require lubricated air to function correctly and prevent wear and seizure of the internal pistons. Always check the manufacturer's manual.
Filtration: The supply air should be clean and dry. A unit that is 2:1 is effectively concentrating any water vapor or contaminants, which can cause issues.
Exhaust: The exhaust port must never be plugged or restricted. When the booster deactivates, the high-pressure air from the output is vented through this port. Plugging it is extremely dangerous.
Flow Rate: Booster valves are not high-flow devices. They are designed for applications that require high pressure but relatively low volume of air. The output flow rate will be less than the input flow rate due to the pressure intensification.
In summary, a VBA Series Booster with a 2:1 ratio is a reliable, purely pneumatic solution for generating medium-high pressures (typically up to 300 PSI) from a standard lower-pressure air supply, controlled by a simple pilot signal.