Principle and Function of Vacuum Pumps
A vacuum pump is a device that uses mechanical, physical, chemical, and other methods to extract gas from an environment with pressure lower than atmospheric pressure and discharge it to the atmosphere. Its main function is to reduce the gas pressure inside a vacuum chamber to achieve the required vacuum level. Vacuum pumps are widely used in industries such as chemicals, electronics, and metallurgy, for processes like accelerating solution filtration, lowering distillation temperature, and speeding up solid drying.
Types of Vacuum Pumps
Common types of vacuum pumps include:
Dry Screw Pumps, Water Ring Pumps, Reciprocating Pumps, Sliding Valve Pumps, Rotary Vane Pumps, Roots Pumps, and Diffusion Pumps. Different pumps are used for different pressure ranges, and they are often combined to meet specific needs.
Working Principles of Vacuum Pumps
Water Ring Vacuum Pump: The rotating impeller throws water to form a water ring, and the intake space is gradually compressed, leading to gas discharge.
Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump: An oil-sealed pump, used for low vacuum, it works by compressing the gas between the vanes and pump housing and then discharging it.
Roots Vacuum Pump: Similar to a Roots blower, gas is sucked into the space between the rotors, and without compression, it is directly discharged out of the pump.
Applications of Vacuum Pumps
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various processes, such as:
Chemical Production: Improving solution filtration speed, lowering distillation temperature, and preventing decomposition during high-temperature distillation.
Drying Solid Materials: Lowering temperature to accelerate the drying process.
Heat Exchangers: Speeding up heat exchange after the heat pipe is evacuated.
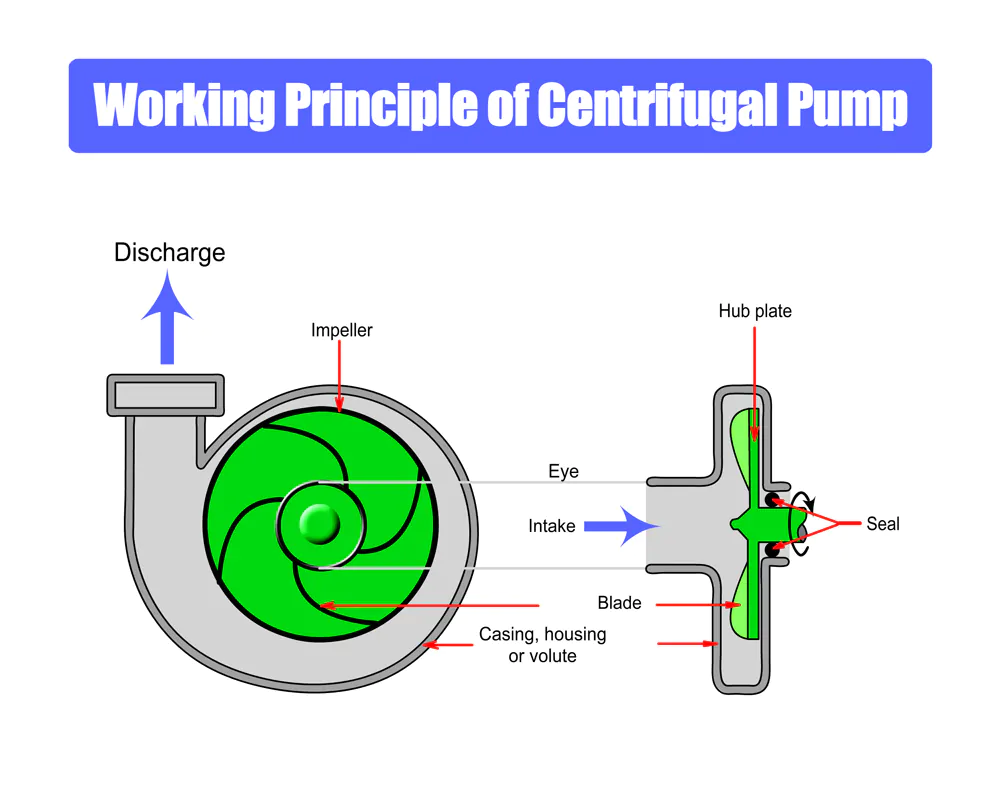
Choosing a Vacuum Pump
The selection of a vacuum pump depends on the required vacuum level:
Water Pumps: Suitable for applications that do not require very low pressures.
Oil Pumps: Can achieve lower vacuum (e.g., 0.133 Pa) and are suitable for more precise experiments.
Diffusion Pumps: Ideal for applications requiring high vacuum (below 0.133 Pa).
The efficiency of a vacuum pump depends on its structure and the quality of the oil. When using a vacuum pump, it is important to choose the right type based on the gas being pumped to avoid damaging the pump.