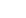
Förståelsen av en luftförråd tankens struktur
Lufttankar spelar en avgörande roll i komprimerade luftsystem. Att förstå deras konstruktion bidrar till säkerhet, effektivitet och lång livslängd.
1. Tankskal: Kärnkomponenten
Tankskalet utgör huvuddelen av en lufttank. Det lagrar komprimerad luft och tål det inre trycket kontinuerligt.
Kolstål och rostfritt stål används ofta. Kolstål är lämpligt för de flesta industriella applikationer, medan rostfritt stål passar fuktiga miljöer samt livsmedels- och läkemedelsindustrier. Skalts tjocklek påverkar direkt säkerheten och livslängden. Korrekt design av skalet uppfyller kraven på arbetstryck och överensstämmer med säkerhetsstandarder.
2. Slagytor (ändskivor): Viktiga spänningsområden
Slagytor, vanligtvis ellipsformade eller kupolformade, sprider det inre trycket jämnt. Dessa komponenter utsätts för de högsta spänningsnivåerna. Felaktig formning eller svetsning i slagytor kan leda till förtida brott. Välkonstruerade ändskivor förbättrar strukturell integritet och minskar materialutmattning över tid.
3. Munstycken och anslutningar: Viktiga kopplingar
Lufttankar innehåller flera munstycken och anslutningar, såsom:
Lufthållare
Luftuttag
Avloppsanslutning
Säkerhetsventilanslutning
Manometeranslutning
Korrekt placering och tillräcklig förstärkning runt munstycken förhindrar läckage och säkerställer systemets pålitlighet.
4. Avloppssystem: Förhindra inre korrosion
Vatten samlas naturligt i lufttankar. Otillräckligt avlopp försämrar korrosionen. Ett avlopp placerat i det lägsta läget, helst automatiskt för kontinuerliga system, förlänger tankens livslängd. Korrekt avlopp är ofta viktigare än materialval för långsiktig hållbarhet.
5. Stödstruktur: Säkerställa stabilitet
Vertikala tankar använder vanligtvis ben eller kjolar; horisontella tankar använder sadlar. Korrekt stöd förhindrar vibrationer, ojämn belastning och strukturell skada. Stabila grundläggningar skyddar tanken och den anslutna utrustningen.
6. Säkerhetsutrustning: Integrerad design
Strukturell design måste ta hänsyn till säkerhetsanordningar, inklusive:
Säkerhetsventil
Tryckmätare
Inspektionsluckor eller manskåpor
Att bortse från dessa komponenter försämrar säkerheten. Riktig design förenklar inspektion, underhåll och testförfaranden.
Slutsats
Konstruktionen av en tryckluftsbehållare avgör dess säkerhet, driftsprestanda och livslängd. En omfattande utvärdering av skalet, ändtäckena, munstycken, avlopp och stöd säkerställer tillförlitlig funktion. Att förstå dessa strukturella delar hjälper industrier att optimera val, drift och underhåll av tryckluftsbehållare.