پمپهای حلقه آبی: اصل کار، قطعات و کاربردها
پمپهای حلقه آبی از نوع پمپهای جابجایی مثبت هستند که از یک حلقه آب در حال چرخش برای ایجاد محفظه در بسته استفاده میکنند و بهصورت کارآمد مایعات یا گازها را منتقل مینمایند. این پمپها بهویژه در صنایعی که نیاز به کنترل پایدار دبی و فشار دارند، و همچنین در کاربردهای ترابری گاز یا مخلوط گاز و مایع، کاربرد گستردهای دارند.
پمپ حلقه آبی چیست؟
آمپر پمپ حلقه آبی به این ترتیب کار میکند که از یک حلقه آب تشکیلشده در داخل پوسته پمپ برای ایجاد محفظهای با حجم متغیر استفاده میکند. تغییر حجم این محفظه به مکش و خروج سیال یا گاز کمک میکند.
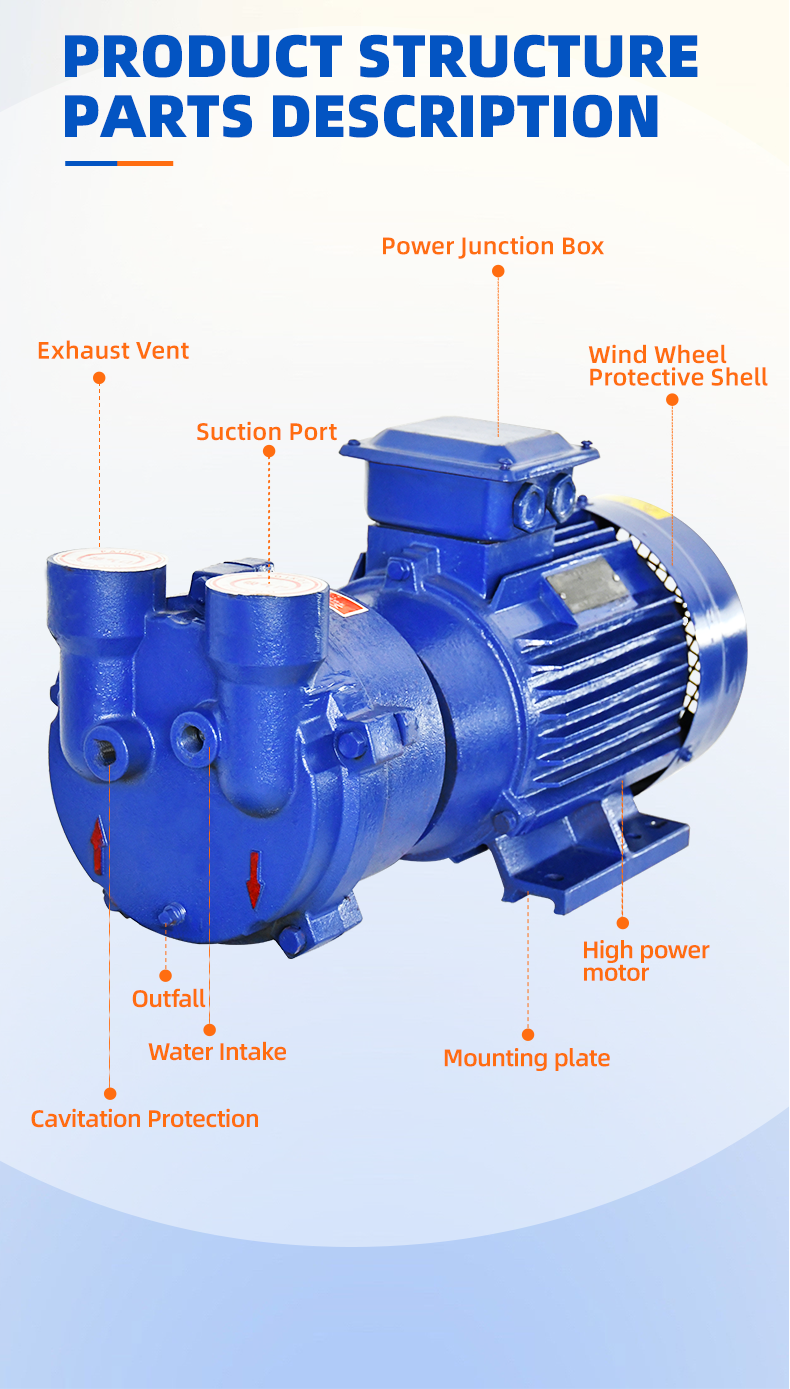
اجزای کلیدی شامل:
پوسته پمپ : شامل حلقه آب در حال چرخش است.
توربین : حرکت حلقه آب را به راه میاندازد.
حلقه آب : محفظهای در بسته را برای جابجایی سیال ایجاد میکند.
بلبرینگها و آببندی : عملکرد روان را تضمین کنید و از نشتی جلوگیری کنید.
چگونه کار میکند
میزان شیرجه : پروانه چرخان یک خلأ ایجاد میکند و سیال یا گاز را به داخل پمپ میکشد.
فشردهسازی : هنگامی که حجم محفظه کاهش مییابد، سیال یا گاز متراکم میشود.
گسیل : سیال یا گاز متراکم شده از طریق خروجی خارج میشود.
عملیات مداوم : این فرآیند با ادامه چرخش پروانه تکرار میشود.
کاربردها
پمپهای حلقه آبی معمولاً در موارد زیر استفاده میشوند:
سیستمهای خلاء (صنایع شیمیایی، دارویی)
انتقال گاز (بازیابی گاز، سیستمهای کمپرسور هوایی)
پردازش آب فاضلeh
انتقال مواد غذایی و نوشیدنی (مثلاً، شیر، آبمیوه)
پردازش شیمیایی (برای مایعات خورنده)
نتیجهگیری
پمپهای حلقه آبی قابل اعتماد، کارآمد و همهکاره هستند و بهویژه در صنایعی با فشارهای متغیر یا سیالات دارای ناخالصی، برای انتقال گازها و مایعات ایدهآل میباشند.